Frequency And Gain Relationship . In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. The frequency response depends directly on the components. As frequency increases, gain decreases, with the prominent transition from stable gain to. In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases. Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to its input. As you might have guessed, this parameter is the gain. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle \(\phi (\omega)\) that is the. In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver a constant and acceptable level of gain.
from www.prosoundweb.com
As frequency increases, gain decreases, with the prominent transition from stable gain to. Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to its input. The frequency response depends directly on the components. In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver a constant and acceptable level of gain. In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. As you might have guessed, this parameter is the gain. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle \(\phi (\omega)\) that is the. In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases.
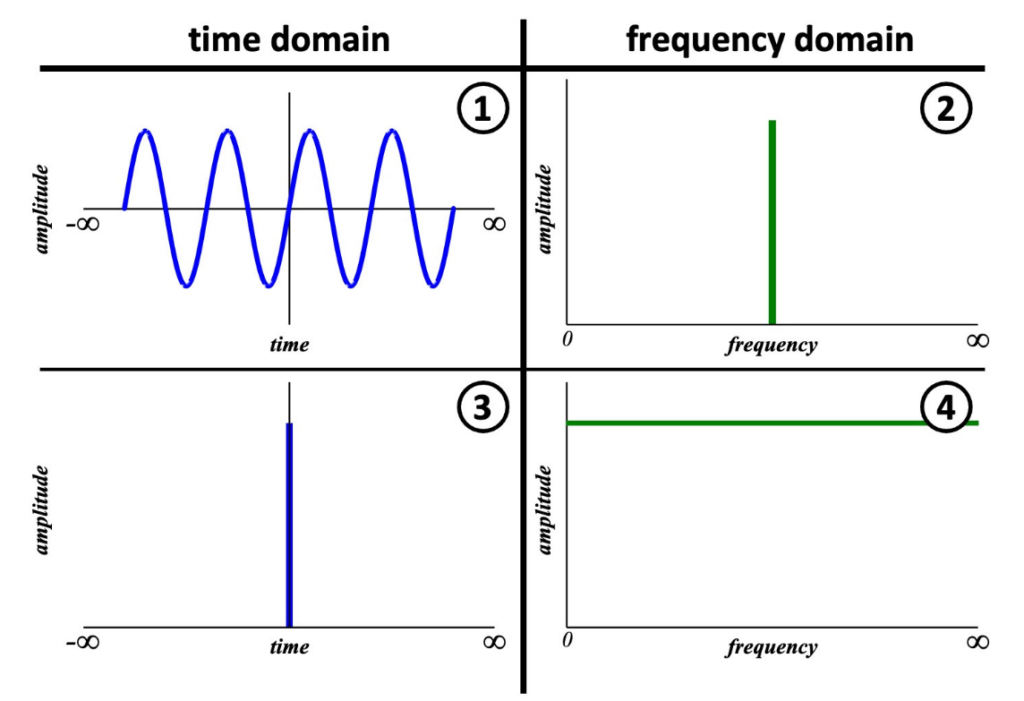
A Group Of Frequencies The Relationship Between Time & Frequency
Frequency And Gain Relationship Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to its input. In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases. In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver a constant and acceptable level of gain. In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. The frequency response depends directly on the components. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle \(\phi (\omega)\) that is the. Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to its input. As frequency increases, gain decreases, with the prominent transition from stable gain to. As you might have guessed, this parameter is the gain.
From chart-studio.plotly.com
Voltage Gain ( dB ) vs Frequency made by Jabir plotly Frequency And Gain Relationship Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to its input. In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Basic Antenna Theory and Concepts PowerPoint Presentation, free Frequency And Gain Relationship As frequency increases, gain decreases, with the prominent transition from stable gain to. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle \(\phi (\omega)\) that is the. In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.researchgate.net
Gain vs. frequency response of the differential current amplifier for Frequency And Gain Relationship In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver a constant and acceptable level of gain. In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. As frequency increases, gain decreases, with the prominent transition from stable gain to. Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From chart-studio.plotly.com
Gain vs Frequency line chart made by Matlabdemos plotly Frequency And Gain Relationship Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to its input. In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases. In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver a constant and acceptable level. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From itecnotes.com
Electrical Gain at Break frequency of OpAmp Valuable Tech Notes Frequency And Gain Relationship In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. As you might have guessed, this parameter is the gain. As frequency increases, gain decreases, with the prominent transition from stable gain to. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From chart-studio.plotly.com
Gain / dB vs Frequency / Hz scatter chart made by Frequency And Gain Relationship The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle \(\phi (\omega)\) that is the. In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases. As you might have guessed, this parameter is the gain. The. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.researchgate.net
Unitycurrentgain frequencies (fT) of nand pMOSFET's versus channel Frequency And Gain Relationship In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver a constant and acceptable level of gain. In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases. Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.pinterest.com
1c. It shows the relationships between the frequency, wavelength, and Frequency And Gain Relationship In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver a constant and acceptable level of gain. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle \(\phi (\omega)\) that is the. As you might have guessed, this. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.researchgate.net
The measured gain diagram vs frequency Download Scientific Diagram Frequency And Gain Relationship In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases. The frequency response depends directly on the components. As you might have guessed, this parameter is the gain. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.researchgate.net
The simulated and measured gain at different frequencies Download Frequency And Gain Relationship The frequency response depends directly on the components. In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle \(\phi (\omega)\) that is the. As frequency increases,. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.researchgate.net
The measured gain versus frequency plot Download Scientific Diagram Frequency And Gain Relationship In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver a constant and acceptable level of gain. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle \(\phi (\omega)\) that. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From rebeccamrobinsonxo.blob.core.windows.net
Is Frequency The Same As Amps Frequency And Gain Relationship As you might have guessed, this parameter is the gain. In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to its input. The frequency response depends directly on the components. As frequency increases, gain decreases, with the. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.researchgate.net
Frequency response of two‐stage operational amplifier showing gain plot Frequency And Gain Relationship The frequency response depends directly on the components. In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle \(\phi (\omega)\) that is the. In the frequency. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From journals.physiology.org
The forcefrequency relationship insights from mathematical modeling Frequency And Gain Relationship The frequency response depends directly on the components. In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases. In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver a constant and acceptable level of gain. As you might have guessed, this parameter is the. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.researchgate.net
Gain Vs Frequency plot of proposed Antenna Download Scientific Diagram Frequency And Gain Relationship In other words, the gain decreases at the same rate at which the frequency increases. The frequency response depends directly on the components. As you might have guessed, this parameter is the gain. Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to its input.. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.researchgate.net
Simulated and measured gain at the various frequencies. Download Frequency And Gain Relationship In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to its input. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.researchgate.net
The relationship between DC gain and switching frequency Download Frequency And Gain Relationship In the frequency range that amplifiers have been designed for, they must deliver a constant and acceptable level of gain. In figure 5.3.1, the product is 1 mhz. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the input sinusoid and a phase angle \(\phi (\omega)\) that. Frequency And Gain Relationship.
From www.researchgate.net
Gain vs. frequency. Download Scientific Diagram Frequency And Gain Relationship As you might have guessed, this parameter is the gain. Generally, the frequency response analysis of a circuit or system is shown by plotting its gain, that is the size of its output signal to its input. The frequency response is expressed as a gain or magnitude \(m(\omega)\) that is the ratio of the amplitude of the output to the. Frequency And Gain Relationship.